NOI '99 P4 - Chessboard Division
View as PDFNational Olympiad in Informatics, China, 1999
An chessboard is divided as follows: Cut out one rectangular section
such that the remaining section is also rectangular. Continue cutting
the remaining section again in this fashion. After making
cuts, there should be
remaining rectangular sections of the
chessboard. Each cut may only be made on grid-lines of the board.
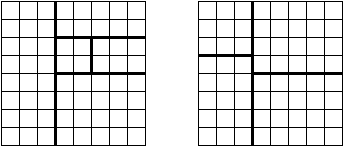
The first figure above is an example of an acceptable cutting method, while the second figure above is an example of an unacceptable cutting method.
Each cell in the original chessboard has a score value, and the score
value of any rectangular division is the sum of the scores of all of the
cells that it contains. Now we must divide the chessboard into
rectangular sections using the method above, while minimizing the mean
squared error of the scores of each section.
The mean squared error (MSE)
, where the
mean
, and
represents the
score of the
-th board division.
Write a program that, given the scores of cells on the chessboard and
the number of divisions , finds the minimum possible value of
.
Input Specification
The first line of input contains the integer
. Line 2
to line 9 of input each contain 8 non-negative space-separated integers
less than 100, describing the score values of each cell on the
chessboard.
Output Specification
The output should contain the single number , rounded and displayed to
three digits after the decimal point.
Sample Input
3
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 3Sample Output
1.633Explanation
The sample input corresponds to the chessboard below.
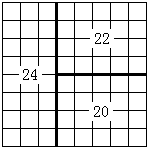
Problem translated to English by .
Comments