COCI '19 Contest 2 #2 Slagalica
View as PDFLittle Fabian got a one-dimensional jigsaw puzzle that consists of pieces. He quickly realized that each
piece belongs to one of the following types:
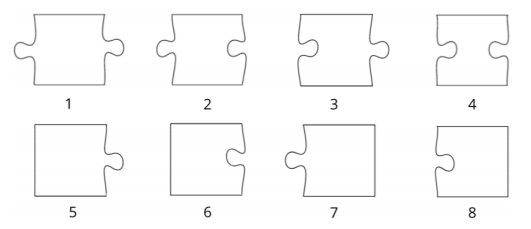
Additionally, it is known that among those pieces there is exactly one piece of either type
or type
(left border) and exactly one piece of either type
or type
(right border).
Fabian wishes to arrange all of the pieces into a single row such that the first (leftmost) piece is of type
or
and the last (rightmost) piece is of type
or
. Two pieces can be placed next to each other if and
only if their neighbouring borders are of different shapes, i.e., one has a bump (also called outie or tab)
and the other has a hole (also called innie or blank).
Simply solving the puzzle would be too easy for Fabian so he decided to write a unique positive integer on
each of the pieces. Now he is interested in finding the lexicographically smallest solution to the jigsaw
puzzle. The solution is considered lexicographically smaller than solution
if at the first position
(from the left)
where they differ it holds that the number written on
-th puzzle in
is smaller than the
number written on
-th puzzle in
.
Note: the pieces cannot be rotated.
Input
The first line contains an integer
from the task description.
The next lines contain two integers
and
which represent the type
of the
-th piece and the number Fabian wrote on it. All numbers
will be different.
Output
If Fabian cannot solve the jigsaw puzzle, you should output -1 in a single line.
Otherwise, you should output the numbers that are written on the pieces in the lexicographically smallest solution to the puzzle.
Scoring
In test cases worth a total of points it will hold
.
In test cases worth additional points it will hold
.
In test cases worth additional points pieces of types
and
will not appear in the input.
In test cases worth additional points there will be at most one piece of type
or
.
If for some test case in which the solution to the puzzle exists, you output the correctly solved puzzle but
your solution is not lexicographically smallest, you will get of the points intended for that test case.
Sample Input 1
5
1 5
2 7
2 3
8 4
6 1Sample Output 1
1 3 7 5 4Explanation For Sample 1
There are only two possible solutions to the puzzle:
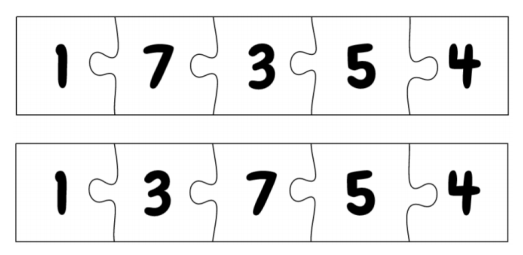
We can see that the second depicted solution has a smaller number written on the second piece. Therefore, that is the lexicographically smallest solution.
Sample Input 2
3
5 1
7 2
4 3Sample Output 2
1 3 2Sample Input 3
5
2 5
2 7
2 3
8 4
6 1Sample Output 3
-1
Comments